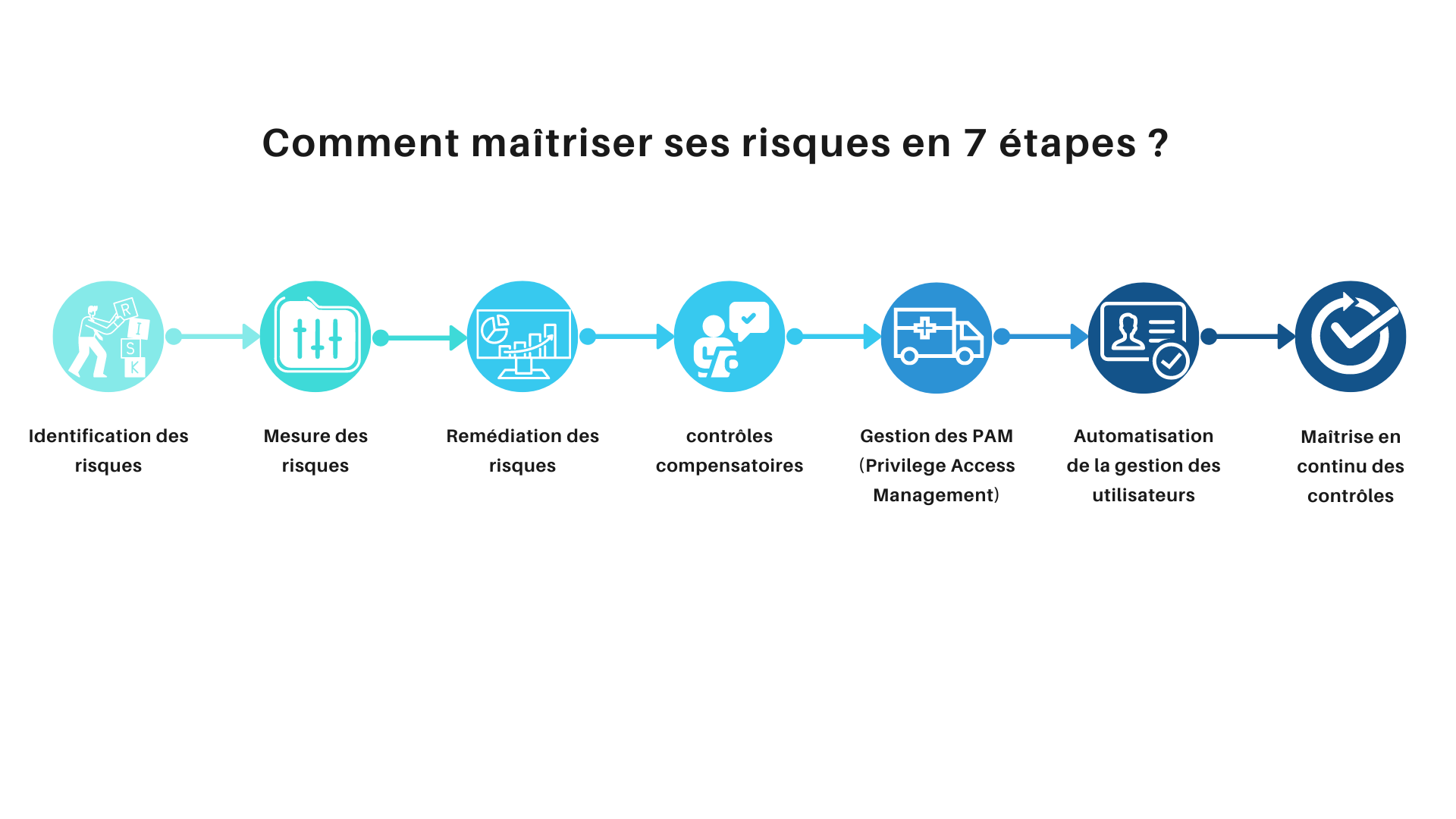
What if reducing the risks associated with your SAP authorizations and maintaining compliance over time was simple?
Organizations are forced to increase their vigilance to minimize the possibility of error, fraud or malfeasance that could damage financial data or the confidence of employees, shareholders and investors.
Very often, in the observed frauds, the danger comes from the inside, from the users who accumulate too many rights allowing them to act in all peace...
- Identification of risks
To keep control of risks (SoD: Segregation of Duties and sensitive actions) and meet auditors' expectations, it is essential to define this matrix.
But it is just as important to think about integrating the possible flows that you plan to implement and especially the functions that you consider critical or sensitive, without forgetting your specific developments.
To avoid obtaining numerous unproven risks ('false positives'), it is imperative that the composition of the actions making up the risk be as fine as possible.
Don't neglect it, each organization is different and the risks that apply to some do not necessarily apply to others!
- How to measure your risks?
You now have a risk matrix that corresponds to your regulatory constraints, this is a very good start, what remains is to choose a solution with a risk analysis engine, fast and powerful because it is not possible to measure them manually.
The speed of calculation and the customization capabilities of the reports and dashboards will allow you to have different levels of analysis depending on the interlocutors.
Indeed, a consultant in charge of the remediation of roles and users will need very detailed analyses, whereas managers and sponsors will more naturally tend towards synthetic reports summarizing the progress of the project and the evolution of risks globally!
The possibilities of integration into your system landscape is another criterion that should not be neglected if you plan to interface with other software in the future...
The solution SWAWE RISK performs a real time reading of the authorization information in SAP. The information is therefore always up-to-date and reliable. In addition, SWAWE RISK allows you to process this information quickly to get a synthetic view in the form of reports, graphs or dashboards.
- Risk remediation
You now have the first result showing your level of exposure to risks, it's perfect, but based on this more or less alarming finding, what should be done to quickly improve this situation?
Do the roles distributed to users make it possible to respect these constraints of separation of duties and control of access to critical functions?
The answer seems obvious when you realize that individual roles alone accumulate a certain number of SoD risks (for example, a role giving access to 10 functions in the matrix will have to be separated into a minimum of 10 distinct roles to ensure a good functional distribution, not to mention operational constraints), having roles without SoD risks is a prerequisite for the success of a remediation approach!
If the number of "at risk" roles is too high, a redesign is required...
We have seen a 60% reduction in SoD risk by simply giving users conflict-free roles.
It will then be necessary to make the effort at the user level to continue this risk reduction according to the organization's capabilities, and then to put in place compensating controls for the accepted residual risks.
Do not hesitate to consult our customer cases!
- Which compensatory controls for which risks?
You have reached an acceptable level of risk, but now you have to prove that it is perfectly under control!
Very often, we find that clients already have internal procedures that perfectly cover these residual risks, so all that remains is to identify and describe them to satisfy the auditors (and make sure they are properly done, but we'll talk about this again in point 7).
There are also certain functionalities in SAP® that can help you control certain sensitive functions natively (such as the implementation of "Dual Control" to systematize the validation of sensitive data changes in customer and supplier files).
Read our use case: Follow up on audit recommendations and prove it to the auditors
- Implement a PAM (Privilege Access Management) tool
Often, wider accesses are retained for reasons of comfort and urgent operational needs.
Indeed, there is no question of blocking an accounting closure or the interventions of administrators for lack of rights.
There are Privileged Rights Management (PRM) solutions that not only allow you to transfer the rights your users need on an ad hoc or urgent basis (with or without an approval workflow), but also to add additional controls: all actions performed are traced and logged in the tool so that they can be reviewed and controlled later.
So why deprive yourself of it if it allows you to further reduce the risks of your users while guaranteeing the autonomy of your users?
Look at the solution SWAWE PAM for more information.
- Automation of user management
Now that all your risks are reduced and under control, how can you avoid new drifts?
By implementing an automated user management solution!
In addition to the return on investment, these solutions will bring you a significant gain in processing time, user satisfaction and risk control with the implementation of preventive simulation.
Managers in charge of validating requests are informed of the impact in terms of risk of the current request according to the user's existing rights.
With the traceability of this type of solution, you also eliminate the problems of delays in archiving accounts (if the information comes from a data source such as HRIS) and you significantly improve your ability to respond to auditors' expectations!
- Continuous control of controls
And finally, the ultimate solution that will allow you to optimize the supervision of your controls, the CCM (Continuous Control Monitoring).
Whether it be compensatory controls, RGPD, SAPIN2, SOX, ITGC, etc., the CCM allows you to materialize these controls in the form of a list of periodic tasks so that they are assigned to the dedicated contacts and carried out on time (if not, a reminder and escalation procedure can be customized).
Once the control is done, the result is stored and the whole life cycle of each task remains accessible with dashboards ensuring a perfect follow-up.
Finally, the level of compliance is also guaranteed by this process, so why not?
The case of our client ARAYMOND might be of interest to you.